Back in the day, the phrase "The American Way of Death" invoked
Jessica Mitford's classic
expose of the funeral industry. In bioethics and law, however, it has a more immediate connotation. With 80% of all Americans dying in an insitutional setting, what is the meaning of "a good death"? And is it possible to achieve in a hospital? Palliative care services notwithstanding, the standard of care for a dying patient typically leaves a lot to be desired. Just how much is well illustrated in an article in the June 21 issue of JAMA (subscription required):
"At Face Value" by
Karen Donley-Hayes. In discussing her best friend Ashley's death at 36 of breast cancer, she described a process all to familiar to those of us who hang around hospitals:
In Ashley's care (with which I have no quarrel), there was no focus on dying until — reluctantly — she went into hospice two weeks before the end of her life. Fortunately, hospice did give us all some preparation for what was to come, but I recall no substantive discussion with the oncologist, or the nursing staff, or the surgeons about what to expect as Ashley died, how to handle it, and what to do — only discussions about how to fight the cancer, until it was clear that fighting was over. Then, it seemed, the entire oncology department removed itself from the picture; even the pain management center seemed to fall short of helping. No one, no organized section of the medical community, came forward to help in the transition from aggressively treating the cancer to helping the patient die. Hospice stepped up to the plate within the scope of its purview, but the medical community, in retrospect, seemed to have hit a wall, as if their jurisdiction to help Ashley in any way ended when it was clear that she would die.
Ashley liked and respected her physicians, liked the nurses who helped with her chemotherapy; for the year and a half of her illness, these people had become, in a way, a part of her family. They knew her by name, knew about her life, what she did, what she liked, her family. For a while, she saw and talked to them nearly as much as the rest of her family. And suddenly, they were gone. Out of the picture. Part of her past. One nurse came to Ashley's memorial service, a gesture that showed us that Ashley had been important to them too; other than that, I did not see any of the members involved in her medical care again. While they were trying to beat this cancer, to win the battle, they were there en masse. When no more chemotherapy or radiation would be administered, they were gone. Looking back, I see this as a sad departure, almost an abandonment. They were there to help her try to live, but they were not there to help her die. . . .
Ashley's situation was unique, because she had several people in her immediate family and close circle of friends who were able to devote themselves to her during her illness and dying process. As time has passed since her death, and I have studied medical ethics and end-of-life issues, it has become clearer to me that there is a gap in the scope of medical care for terminally ill persons: How does the medical community help people die? Can the physicians who govern the treatment of an illness also embrace the care of the patient and the patient's family in the dying process? The disconnect that happens when the "fight" is over is a disservice to the patient. And it's a disservice to the health care professionals as well. They're out of touch with part of the course of the patient's illness, even if they can't cure the illness.
Ashley was very fortunate in so many ways. But what happens to patients who don't have family and friends with the ability or willingness to help them weather the rigors of treatment, or help them die when and if the time comes? Who supports these patients? Who helps their families and friends, who must try and manage this with little or no training or guidance?
Hospice can be a huge help, but it's still a blunt separation from the medical teams that were treating the patient. The transition in care might be the flick of a light switch, but the transition in terms of spirituality, psychology, acceptance for the patient — or the patient's family — cannot be so simple.
If the act of dying isn't shuttled into the closet, if the medical community could embrace it as a natural part of life, the process could be an easier one on everyone — less frightening, less painful, less lonely and rudderless. Death is ugly, scary, and final. But I doubt that any of us want to die feeling impotent, abandoned, no longer in the embrace of the physicians who cared for us when they hoped we might live. A natural part of death for everyone is grief, anxiety, fear, maybe anger. But it can also be a time of growth and enlightenment.
Ashley wasn't timid about dying. The medical profession shouldn't be either.
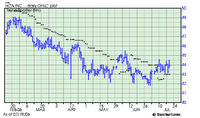
 The closing probably won't be till the 4th quarter, assuming the federal regulators bless it and the board doesn't get a better offer, but HCA's board has approved the sale of the company to an aglomeration of investment bankers and the founding Frist family. Of course, no one can quite agree whether the deal is worth $21 billion, $31 billion, or $33 billion, but what's a few billion here or there?
The closing probably won't be till the 4th quarter, assuming the federal regulators bless it and the board doesn't get a better offer, but HCA's board has approved the sale of the company to an aglomeration of investment bankers and the founding Frist family. Of course, no one can quite agree whether the deal is worth $21 billion, $31 billion, or $33 billion, but what's a few billion here or there?